Distribution Management: Streamline Your Supply Chain for Peak Efficiency
Distribution management handles the flow of goods in the supply chain. It covers everything from raw materials sourcing to order fulfillment. This article breaks down distribution management, its perks, and how to nail it. We’ll use real-time tracking, predictive analytics, and digital tools to make it practical.
What is Distribution Management?
Distribution management oversees the movement of goods from suppliers to customers. It includes distribution channels, inventory management, and logistics management. Think of it as the backbone of the supply chain.
It’s not just about shipping. It involves order processing, warehouse operations, and material handling. For manufacturing organizations, it starts with raw materials sourcing. In modern retail, it meets retail demands through multi-channel inventory management.
Distribution management systems help track stock levels and inventory levels. They boost customer satisfaction by speeding up delivery.
Why Distribution Management Matters
Strong distribution management cuts costs and lifts profits. It leads to cost savings through better inventory control and optimized transportation routes. It improves customer service. Fast order fulfillment builds loyalty. Without it, delays hurt customer satisfaction. In global supply chains, it handles international DIT and Federal transportation regulations. It keeps businesses competitive in fast-paced markets.
How Distribution Management Works: The Process
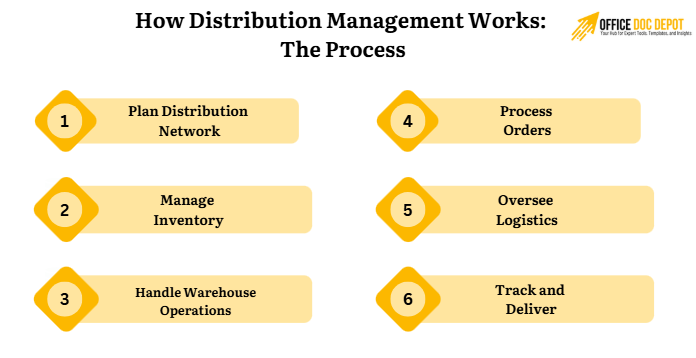
Distribution management follows a clear process. Here’s the breakdown:
- Plan Distribution Network: Set up distribution channels. Choose mass strategy, selective strategy, or exclusive strategy based on products.
- Manage Inventory: Use inventory management to track stock levels. Avoid overstock or shortages with inventory control.
- Handle Warehouse Operations: Optimize warehouse layout and warehouse locations. Use RF Scanning and warehouse management systems for efficiency.
- Process Orders: From purchase order to order picking and order consolidation. Speed up order cycle for rapid fulfillment.
- Oversee Logistics: Cover transportation logistics and distribution logistics. Use private trucking-fleet operations or third-party logistics providers.
- Track and Deliver: Employ real-time tracking and real-time information. Monitor shipping cycle for on-time delivery.
This process fits sales distribution and physical distribution. It aligns with vendor relationship management and customer relationship management.
Types of Distribution Strategies
Choose the right strategy for your business:
- Mass Strategy: Wide distribution for everyday items. Reaches many outlets.
- Selective Strategy: Limited channels for premium products. Builds brand image.
- Exclusive Strategy: One outlet per area. Creates scarcity and loyalty.
These strategies impact distribution network design. They affect how goods move through distribution channels.
Key Components of Distribution Management
Several parts make distribution management work:
- Inventory Management: Tracks inventory turnover and multi-channel inventory management.
- Warehouse Operations: Involves centralized warehouse or TSA-cleared facility. Uses advanced management systems for material handling.
- Logistics Management: Handles 3rd Party Logistics, Amazon FBA, and transportation management systems.
- Order Fulfillment: Covers order processing, order picking, and rapid fulfillment.
- Customer Service: Boosts satisfaction with data-driven sales insights and market intelligence.
Regulatory adherence is key. Follow Federal transportation regulations and get E&O coverage.
Tools for Distribution Management
Modern tools make distribution management easier. Use distribution management systems for full control.
- Warehouse Management System: Tracks warehouse operations. Examples include Acctivate Inventory Software.
- Transportation Management System: Optimizes transportation routes. Integrates with API integration.
- Digital Tools: Like Microsoft’s Azure for cloud storage. Enables predictive analytics and real-time information.
- Other Software: Nexus repository for data. Payment processors for smooth transactions.
These tools support outage management and rate adjustments. They work with commission plans for sales teams.
Supply chain analysts use them for insights. Tools like Freeport Center or Distribution Management AAS help train staff.
Distribution Management in Action: Examples
Supply Chain
In supply chain, distribution management moves goods efficiently. A produce distributor supplies fresh items to stores. They use real-time tracking to keep quality high.
Modern Retail
Retailers like online shops use Amazon FBA for storage and shipping. It meets retail demands with fast delivery. Multi-channel inventory management handles online and in-store sales.
Global Supply Chains
For global supply chains, companies use third-party logistics providers. They handle international DIT and customs. Predictive analytics forecasts demand spikes.
Manufacturing organizations source raw materials worldwide. They optimize distribution services for cost savings.
Challenges in Distribution Management
Distribution management faces hurdles:
- Inventory Issues: Wrong stock levels lead to waste.
- Logistics Delays: Bad transportation routes slow delivery.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Federal transportation regulations complicate things.
- Customer Demands: High expectations for rapid fulfillment.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Outages or vendor problems.
To fix these, use background checks for staff and vendor relationship management.
Best Practices for Distribution Management

Follow these tips for success:
- Track Everything: Use real-time tracking for visibility.
- Automate Processes: Implement warehouse management systems.
- Optimize Inventory: Monitor inventory turnover with predictive analytics.
- Build Vendor Programs: Set up compliance for smooth operations.
- Train Staff: Use incentives to boost productivity.
- Focus on Customers: Use data-driven sales insights for better service.
- Stay Compliant: Follow regulatory adherence and get E&O coverage.
In warehouse operations, improve layout for faster material handling. For order fulfillment, shorten order cycle with order consolidation.
These practices come from experts. They include setting KPIs and assessing operations.
Future Trends in Distribution Management
Distribution management evolves fast. Key trends for 2025:
- AI and Machine Learning: Predict demand and optimize routes.
- Sustainability: Focus on ethical sourcing and green logistics.
- Cloud Systems: Adopt cloud WMS and TMS for flexibility.
- Automation Growth: More robots in warehouses.
- Diversified Networks: Build resilient supply chains.
These trends help handle disruptions. They use blockchain for transparency.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is distribution management?
It oversees goods movement in the supply chain. It includes inventory management and logistics.
Why is it important?
It cuts costs, boosts customer satisfaction, and improves efficiency.
What tools help?
Warehouse management systems, transportation management systems, and digital tools like Microsoft’s Azure.
How does it work in supply chain?
It optimizes distribution channels and order fulfillment for smooth flow.
What are common challenges?
Inventory issues, delays, and regulatory hurdles.
How to improve it?
Use best practices like automation and real-time tracking.
Conclusion
Distribution management is key to supply chain success. It aligns resources with demand. It cuts costs and keeps customers happy. Whether in modern retail or global supply chains, it drives growth. Use tools, follow best practices, and watch trends to stay ahead. Start optimizing now for a stronger business.
-
The Super Smart Bundle (all my financial models)
If you want access to my entire library of templates, this is the most discounted way to do so. I’ve now got over 200 unique financial models included in this bundle. Learn and sharpen your financial planning.
$ 499$ 999 -
XL Inventory – Inventory, Billing & Profit Tracking
All-in-one Excel system to track stock, create invoices, and see profit at a glance. Automation-ready dashboards, printable docs, and clean workflows — no subscriptions.
$ 199 -
Made to Order Manufacturing Financial Model
This advanced Excel model forecasts the financial performance of a made-to-order manufacturing business over 10 years. It features detailed tracking of accounts payable/receivable, inventory, unearned revenue, accrual/cash accounting, and comprehensive financial statements, including balance sheets.
$ 120 -
General Manufacturing Plant Financial Model
This Excel-based model forecasts the financial performance of a general manufacturing plant over 10 years. It includes detailed revenue and cost calculations based on production units, comprehensive expense modeling, 3-statement financial reports, IRR analysis, cap table management, and exit valuation.
$ 75 -
General Rental Business Financial Model
This Excel-based model forecasts the financial performance of a general rental business over 5 years. It includes detailed revenue calculations based on rental categories and utilization rates, comprehensive expense modeling, 3-statement financial reports, IRR analysis, cap table management, and exit valuation.
$ 75 -
Oil and Gas Wells Financial Model
This Excel-based 20-year financial model allows users to forecast oil and gas well production, costs, and returns. It includes features for modeling multiple well cohorts, exploration, drilling, extraction costs, revenue projections, and a dynamic joint venture waterfall analysis.
$ 70 -
Solar Farm Financial Model
This Solar Farm 20-Year Financial Forecasting Model is a comprehensive tool for projecting the financial performance of a solar farm over two decades. It includes detailed inputs for deployment costs, energy output, seasonality, revenue streams, operating expenses, and financing. Customizable assumptions allow for testing different scenarios with in-depth financial statements, cash flow analysis, and investor returns. This model is ideal for solar developers and investors seeking to evaluate the financial viability of solar farm projects.
$ 60 -
Pareto Analysis
This Excel-based Pareto Analysis template provides a dynamic tool for identifying and prioritizing key areas of improvement across various business functions. It features automated data ordering, conditional formatting, and visual charts to facilitate clear and actionable insights.
$ 45Pareto Analysis
$ 45 -
Manufacturing Process Tracker
This Excel template provides a manufacturing database example for tracking production runs, maintenance records, quality checks, and supplier information. It includes a dashboard for visualizing production efficiency, throughput, and other key performance indicators.
$ 45 -
Retail Sales Scaling Locations Financial Model
This 5-year financial model is designed for scaling up to 25 retail locations, making it ideal for restaurants, home goods stores, or similar businesses. The template includes dynamic logic for variable start dates, capacity growth, multi-ticket revenue streams, labor, and COGS projections. With built-in IRR, NPV analysis, and breakeven calculations, the model ensures precision in forecasting operational scaling and profitability.
$ 45 -
E-commerce Financial Model
This upgraded Excel model forecasts the financial performance of an e-commerce business over 5 years. It includes detailed revenue assumptions, expense modeling, inventory control, 3-statement financial reports, and investor analysis.
$ 45