Logistics: The Lifeline of Modern Business
When most people hear “logistics,” they think of trucks, ships, or warehouses. In reality, logistics is much broader. It’s the coordinated movement of raw materials, inventory, people, and information so that products arrive where they’re needed, when they’re needed, at the right cost and quality.
Put simply: logistics connects businesses to their customers.
Historically, the term came from the military, where moving troops and supplies often determined victory or defeat. Today, it’s no less critical—it determines whether a business can meet demand, deliver on promises, and stay competitive in a fast-paced world.
Why Logistics Matters More Than Ever
In today’s global economy, where a customer in New York expects a product from Shenzhen in just two days, logistics is the engine of customer satisfaction and supply chain success. Companies that master logistics enjoy:
- Stronger customer loyalty through reliable on-time delivery.
- Lower operating costs thanks to efficient inventory management and optimized transportation modes (air, sea, road, rail).
- Better resilience during disruptions like equipment failures, port congestion, or global supply chain shocks.
- A reputation advantage—businesses known for smooth delivery and responsive customer service stand out.
- Sustainability gains from green logistics practices that cut emissions, streamline reverse logistics, and reduce waste.
Core Elements of Logistics
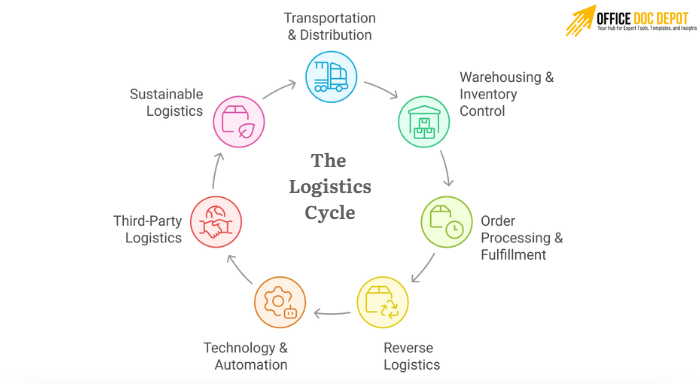
Transportation & Distribution
This is the backbone of logistics, moving goods from suppliers to factories, factories to distribution centers, and centers to customers. Success depends on choosing the right shipping methods, balancing cost with speed, and planning routes intelligently.
Warehousing & Inventory Control
Efficient warehouse management ensures the right goods are stored, tracked, and retrieved when needed. Tools like real-time inventory systems, reorder points, and automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS) help reduce errors and keep inventory levels balanced.
Order Processing & Fulfillment
From the moment a customer clicks “buy,” logistics steps in, coordinating sales order management, order processing, and last-mile delivery to meet promised timelines.
Reverse Logistics
Returns, repairs, recycling, or refurbishing aren’t just afterthoughts, they’re part of modern customer expectations. Done well, reverse logistics can strengthen trust and even create value.
Technology & Automation
Logistics today isn’t manual, it’s digital. Companies use ERP systems, warehouse management systems (WMS), logistics management software, IoT sensors, RFID technologies, and even machine learning to predict demand and optimize supply chains. Robotics like automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and smart conveyors improve workflow planning and throughput.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Not every business wants to run its own fleet or warehouses. Many outsource to third-party logistics providers (3PLs) like DHL, FedEx, or UPS for scalability, expertise, and global reach.
Sustainable Logistics
With rising pressure on businesses to be greener, many are redesigning logistics with eco-friendly packaging, fuel-efficient fleets, and optimized distribution networks that reduce emissions while cutting costs.
Logistics vs. Supply Chain Management
People often confuse logistics with supply chain management (SCM). The difference:
- Logistics = execution. It’s the day-to-day movement, warehousing, and order fulfillment.
- Supply Chain Management = strategy. It covers sourcing, manufacturing, distribution, partnerships, and long-term planning.
In short, logistics is one piece of the supply chain puzzle, but arguably the most visible to the customer.
Future Trends
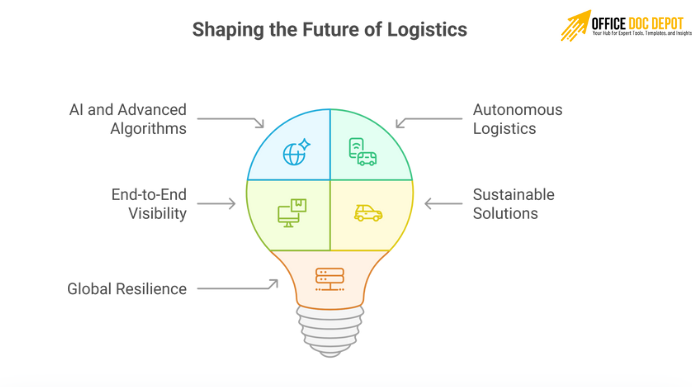
- AI and Advanced Algorithms: Smarter demand forecasting and route optimization.
- Autonomous Logistics: Self-driving trucks, drones, and autonomous scheduling systems.
- End-to-End Visibility: Real-time tracking & tracing, SKU-level visibility, and predictive analytics for delivery times.
- Sustainable Solutions: Shift to renewable-powered fleets, circular supply chains, and green warehousing.
- Global Resilience: Diversifying suppliers and distribution networks to avoid bottlenecks in global supply chains.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between logistics and SCM?
Logistics is about movement and storage. SCM takes a broader view—covering suppliers, manufacturing, distribution, and strategy.
How does logistics improve customer satisfaction?
By ensuring on-time delivery, accurate orders, and responsive customer service, which build trust and loyalty.
Why is reverse logistics important?
It helps businesses handle returns, recycling, and repairs effectively, reducing waste and improving customer experience.
What role does technology play in logistics?
From ERP applications and WMS software to IoT data, technology brings real-time visibility, automation, and efficiency.
What is green logistics?
An approach that reduces environmental impact by optimizing transportation modes, packaging, and energy-efficient warehouse operations.
Conclusion
Logistics is no longer a “back-office” function. It’s a strategic driver of growth, resilience, and customer satisfaction. Businesses that master logistics don’t just deliver products, they deliver confidence, loyalty, and long-term success. In a world where every second and every delivery counts, logistics is not just the movement of goods, it’s the heartbeat of global commerce.
-
XL Inventory – Inventory, Billing & Profit Tracking
All-in-one Excel system to track stock, create invoices, and see profit at a glance. Automation-ready dashboards, printable docs, and clean workflows — no subscriptions.
$ 199